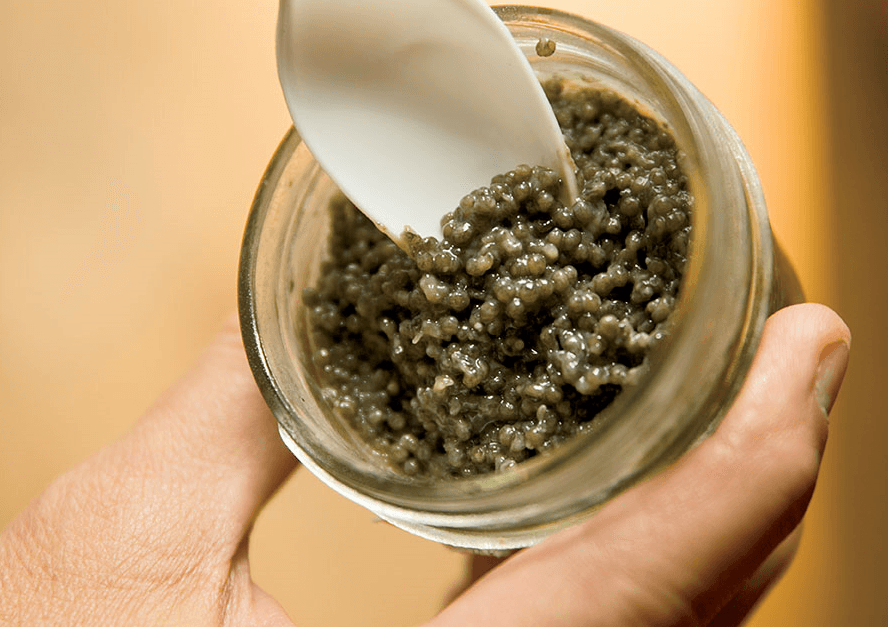
There is chance and need for paddlefish aquaculture to be grown commercially for their meat and roe in the United States based on seeking of two jobs provided at Aquaculture America 2014 in Seattle, composes Lucy Towers, TheFishSite Editor.
Paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) are primitive Chondrostean ray-finned fish that are discovered in freshwater atmospheres in 26 states around America and are strongly valued because of their caviar manufacturing. However, as a reasonably brand-new varieties to aquaculture, the taste and structure of paddlefish meat is not well known by consumers.
Then it might be the following huge meat market and the new catfish of the Southern United States, if paddlefish is well accepted by customers.
A research study by Siddhartha Dasgupta, Kentucky State University, took a look at the success of up and down intergrated paddlefish aquaculture in Kentucky. This system supplied excellent high quality seed stock and also market dimension fish.
Located on a decommissioned reclaimed water treatment plant, the center created 150-200g paddlefish juveniles (stage 2 paddlefish) 6 months after generating. Price of manufacturing was low, around $0.50 / fish.
The Phase II fish were then stocked into ponds using comparable equipping qualities, feeding rates, and feed used in the demanding pond society of stations catfish. After 18 months of growth, the Phase II fish reached a typical valuable dimension of 600g.
In spite of an excellent survival fee of 87 each cent, feed costs were high, making the cost of production around $5.81 / kilograms. Nonetheless, with a 10 each cent rise in feed performance the breakeven price would decrease by five per cent.
Mr Dasgupta also looked at reservoir ranching – substantial manufacturing making use of no feed or synthetic aeration.
This system had a survival fee of 91 each cent. The male expanding season was around three to five months. Females took a little longer – eight to ten months – as it enabled them to create eggs for caviar.
Mr Dasgupta noted that there are some covert prices connected with this manufacturing procedure including harvesting and hauling equipment and handling.
A market research by Alex Philipchik, Kentucky State University, located that 97 each cent of folks liked the flavor of paddlefish and 100 per cent liked that the fish was boneless. Outcomes showed that the Hispanic area favored the fish the most and would want to pay around $6.60 per whole gutted, for the fish.
With 76 each cent of the Hispanic area prepared to pay over the breakeven cost and 71 per cent ready to acquire the entire gutted fish locally, there does appear to be an excellent market need, making paddlefish farming in extensive monculture systems practical.